Semantics is the branch of linguistics that focuses on the study of meaning in a language. It explores how words, phrases, and sentences convey specific meanings within a language and how these meanings can vary in different contexts. Sometimes, you hear a statement that does not make sense, but it has a deep sense. It usually happens with non-native speakers because they only study words in an only literal sense. There are different ways that how a word convey specific meaning within a language. In this article, we will explore important distinctions between literal meaning and non-literal meaning in semantics.
What is Semantics?
Before knowing differences between literal and non-literal meaning, we should know that what is semantic. Semantics is the field of linguistics that deals with the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences in a language. It explores how meanings are constructed, understood, and interpreted by speakers and listeners. Semantics is concerned with both the denotative meanings (literal) and connotative meanings (associative) of a language.
How Semantics Studies Meanings of Words in a Language
Semantics employs various methods to study the meanings of words in a language. It considers the relationships between words, their definitions, and the context in which they are used. Semantics also investigates the roles of syntax and pragmatics in influencing meaning.
Literal Meaning
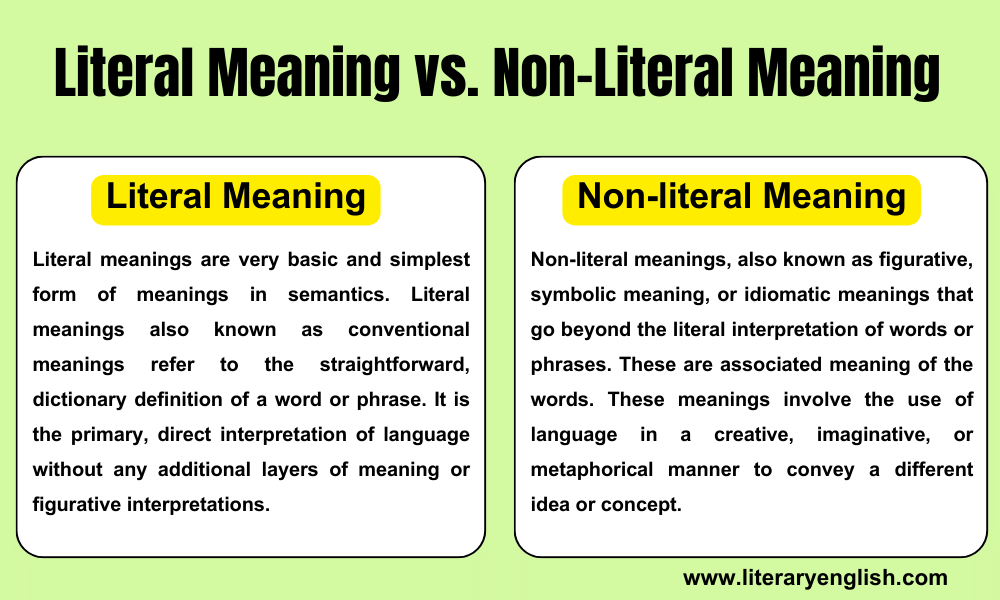
Literal meanings are very basic and simplest form of meanings in semantics. Literal meanings also known as conventional meanings refer to the straightforward, dictionary definition of a word or phrase. It is the primary, direct interpretation of language without any additional layers of meaning or figurative interpretations. Literal meaning is often the most common and basic understanding of a word or phrase. These meanings are also called conceptual meaning.
Examples of Literal Meaning in Sentences
Literal meanings are a description of the word to which it refers to in the real world without any hidden interpretation.
- Adam is reading a book.
- I am feeling hungry.
- The cat is sitting on the mat.
- I love my only son.
- He opened the door and walked inside.
In above examples, all the content words (e.g. reading, book, feeling, hungry, sitting, mat, love, son, door etc.) convey literal meanings. There are no hidden interpretation required to comprehend the intended meaning.
Non-Literal Meanings
Non-literal meanings, also known as figurative, symbolic meaning, or idiomatic meanings that go beyond the literal interpretation of words or phrases. These are associated meaning of the words. These meanings involve the use of language in a creative, imaginative, or metaphorical manner to convey a different idea or concept. Non-Literal Meanings are also called figurative and used in various ways in a language like metaphor, irony, paradox, pun, metonymy, hyperboles, etc. It adds depth, complexity, and richness to communication by allowing speakers to express abstract ideas or emotions in a more vivid and engaging way. Non literal meaning adds aesthetic beauty to the language.
Examples of Non-Literal Meanings in Sentences
In Non-Literal Meanings, speaker deliberately describes something in untrue or impossible terms in order to achieve special effects. For instance:
- Jake is a busy bee.
- Opportunities knock at the door but once.
- She broke my heart when she ended relationship for no reason.
- Time flies when you’re having fun.
- The exam paper was a piece of cake.
In these examples, the phrases “busy bee”, “knock at the door”, “broke my heart,” “time flies,” and “piece of cake” have non-literal meanings. They are used metaphorically to convey emotions, the perception of time, and the ease of a task, respectively. Sometime, non-literal meaning are used to glorify the wording, or to add aesthetic beauty in a language. Understanding these sentences requires interpreting the figurative use of language beyond the literal meanings of the individual words.
Conclusion
Semantics plays a crucial role in understanding how language conveys meaning. It distinguishes between literal and non-literal meanings, highlighting the different layers of interpretation within language. While literal meaning represents the direct, dictionary definition of words, non-literal meanings involve the creative use of language to convey abstract or figurative ideas. By understanding these distinctions, we can navigate the nuances and richness of language more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can a word have both literal and non-literal meanings?
A: Yes, many words have both literal and non-literal meanings, depending on the context in which they are used.
Q: Are idioms considered non-literal meanings?
A: Yes, idioms are a type of non-literal meaning where the figurative use of language creates a different interpretation than the literal meaning of the words.
Related Posts