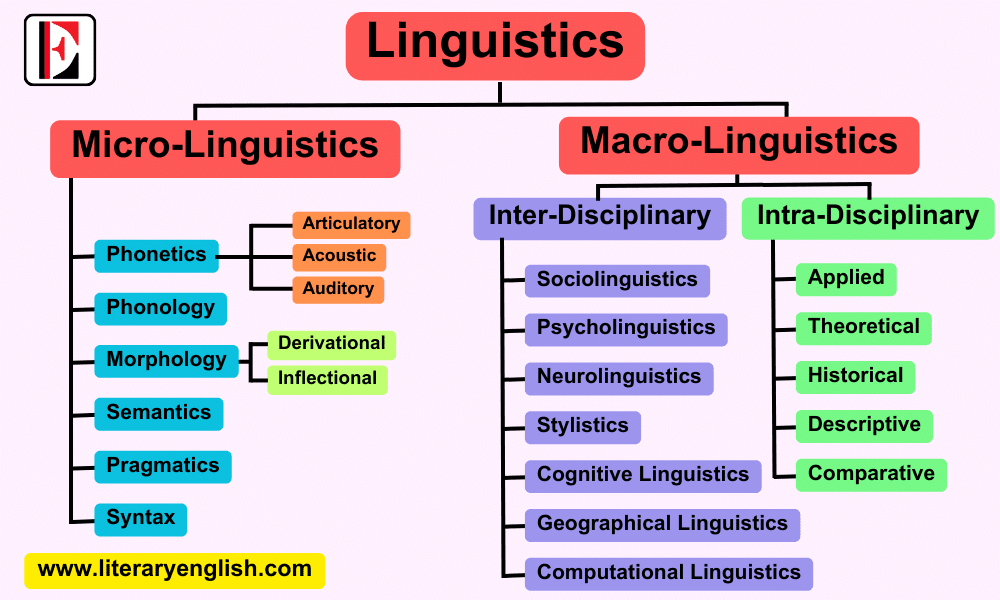
Branches of Linguistics | Micro Linguistics & Macro Linguistics
Linguistics is defined as the scientific study of language. First we should know that what is language? Language is a method of communication across human beings, either written or spoken, consisting of the use of words in a structured way. In simple words, language is a method of expression or communication.
How Robins (1985) defined linguistics
According to Robins (1985), “Linguistics is concerned with human language as a universal and recognizable part of the human behavior and human faculties, perhaps one of the most essential parts of the human life as we know it and as one of the far-reaching of human capabilities, in relation to the whole span of mankind’s achievements.”
Main Branches of Linguistics
From various point of views, linguistics is divided into two main branches:
- Micro Linguistics
- Macro Linguistics
These both branches of linguistics are divide into further various branches. We will discuss all branches with brief definition.
Micro Linguistics and its Different Branches
Micro linguistics focuses on the study of language itself, including its sound (phonetics and phonology) grammatical structures (morphology), syntax, and meanings (semantics) in context (pragmatics).
Phonetics
Phonetics is the study of the sounds of language. It deals with the way sounds are produced, transmitted and perceived by human beings. Phonetics is further divided into three different branches that are:
- Articulatory phonetics: deals with the study of articulation of speech sounds,
- Acoustic phonetics: studies the physical properties of sounds as transmitted from mouth to air and then received by ear drum,
- Auditory phonetics: deals with the study of perpetual response to speech sounds as mediated by ear, auditory nerve and brain.
Phonology
Phonology is the study of how sounds are arranged in each language as organized units of speech. It also looks into the specifications in the distribution of sounds into small sound in each language.
Morphology
Morphology deals with the forms of words, use of words and construction of words by small letters. It studies how words are formed into small meaningful units (morphemes. Morphology is divided into two further branches: inflectional morphology and derivational morphology.
Semantics
Semantics is the study of meaning in a language. It focuses on studying the structure of meaning of words and making a sentence that is meaningful.
Pragmatics
Pragmatics also deals with the meaning of language but is focuses on meaning in context rather than individual word meanings.
Syntax
Syntax is the study of phrase construction, clauses and sentences in a language. It deals with basic word order followed in any languages.
Macro Linguistics
Macro-linguistics takes a broad view of linguistic phenomena, studying language in different context and its development over time. Macro-linguistics includes study of other disciplines that are connected with language study in any perspective e.g. the study of relation between society and linguistics is sociolinguistics.
Macro-linguistics is further divided into Intra disciplinary branches of linguistics and Intra disciplinary branches of linguistics.
Inter Disciplinary Branches of Macro Linguistics
Inter disciplinary branches of linguistics deals with study of linguistics with relation to other disciplines as sociology, psychology, neurology, geography, etc. Below are inter-disciplinary branches of macro linguistics.
Sociolinguistics
Sociolinguistics is generally used for the study of the relationship between society and language. Sociolinguistics is the branch of linguistics that deals with the effect of society on a language. It has strong connections with anthropology, culture, and sociology.
Psycholinguistics
Psycholinguistics deals with the study of the mental aspects of language and speech. Its domain is concerned with how language is represented and processed in the brain. Psycholinguistics, study of linguistics and psychology, is part of the field of cognitive science.
Neurolinguistics
Neurolinguistics deals with the study how language is represented in the brain, how and where a brain stores knowledge of a language that we speak. It focuses on what happens in our brains as we acquire a language, and what happens as we put this knowledge into practice.
Computational Linguistics
Computational linguistics is branch of linguistics that is concerned with the rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective. It is the branch of linguistics that deals with the techniques of computer science that are applied to the analysis and synthesis of language and speech.
Stylistics
Stylistics is an interdisciplinary field of linguistics that deals with the study and interpretation of style and tones in both written and spoken language.
Geographical Linguistics
Geography Linguistic also called dialect geography is study of local or regional variations of a language or dialect studied as a field of knowledge. Language geography is the branch of human geography that studies the geographic distribution of language(s) or its constituent elements.
Cognitive Linguistics
Cognitive linguistics is an interdisciplinary field of linguistics that deals with the study of language, mind, and sociocultural experience that first emerged in the 1970s. Cognitive linguistics is characterized by a commitment to the inseparability of meaning and form in the study of language.
Intra Disciplinary Branches of Linguistics
Intra disciplinary branches of linguistics deal with the study of linguistics within its own discipline. Below are the intra disciplinary branches of macro linguistics.
Theoretical Linguistics
Theoretical linguistics also known as General Linguistics deals with concrete theories presented by scholars of language about various aspects concerning to linguistics. General linguistics is devoted to the theoretical study of describing a language and methods of investigating linguistic phenomena.
Historical Linguistics
Historical linguistics, also called diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of language change over time. Principal concerns of historical linguistics include: how and why language changes, changes in particular languages, history of words i.e., etymology, history of speech communities and relation between different language families.
Descriptive Linguistics
Descriptive Linguistics is concerned with the description and analysis of the ways in which a language operates and is used by a given set of speakers at a given time.
Applied Linguistics
Applied Linguistics examines the structure of language and its role in communication, language acquisition, second language learning, how the social or cultural environment interacts with language, and structure of language and its role in communication.
Comparative Linguistics
Comparative linguistics is an intra disciplinary field of linguistics that deals with comparative study of different languages. It is a sub-branch of historical linguistics that is concerned with comparing languages to establish their historical relatedness. Comparative linguistics is the study of differences and similarities between languages. Particularly it focuses on the comparison of related languages.
You might be interested in…
- What is Linguistics?
- Synchronic Linguistics vs. Diachronic Linguistics
- Relationship Between Linguistics and Other Social Sciences
- Key Characteristics of Language | Human Language
- Human Language vs. Animal Communication
- Causes of Language Change | Types of Language Change
- Linguistics and Applied linguistics | Relationship
- Competence and Performance | Noam Chomsky’s
- Linguistics Functions
- The Concept of Langue and Parole by Saussure
- Applications of Linguistics
- Career of a Linguist