What is Phonology?
Phonology is the main branch of linguistics that deals with the study of the sound system of languages. It focuses on the organization of sounds by studying speech patterns. Phonology is the mental representation of sound sounds as part of a symbolic cognitive system. Phonology is concerned with the range and function of sounds in a specific language unlike phonetic that deals with sounds in
general. Phonology deals with the competence of a speaker that how much a speaker knows about knowledge of the sound system of a language.
Phonology encompasses different aspects like phonetic relationship that relates and contrasts words and other linguistic units, organization of sounds by studying speech patterns and distribution and patterning related to speech sounds. Phonology also answers the questions like – why there is a difference in the plurals of hat and bag; the plural of hat (hats) ends with the /s/ sound, whereas the plural of bag (bags) ends with the /z/ sound.
Branches of Phonology
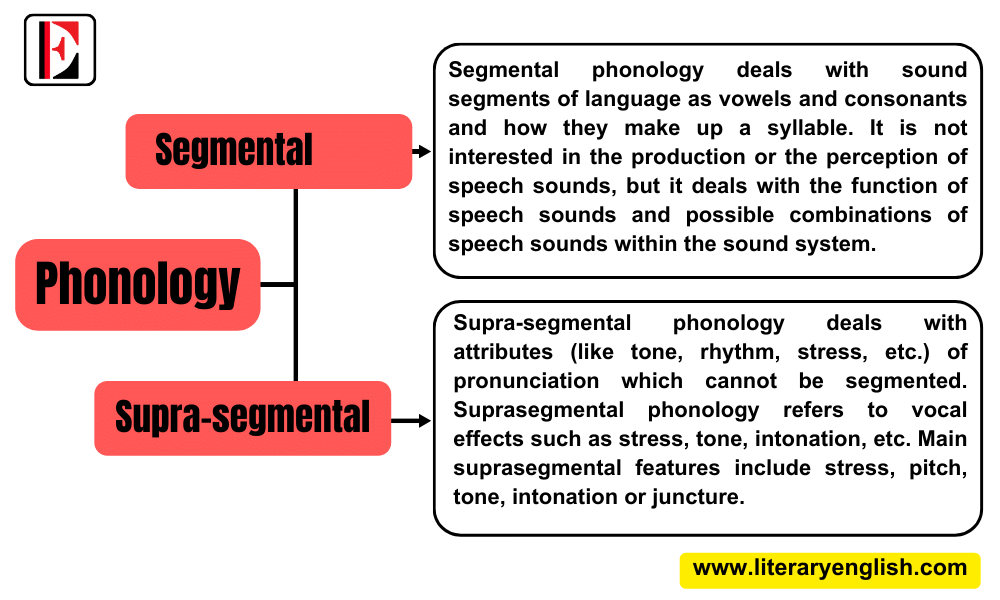
Phonological studies are divided into two main branches:
- Segmental phonology
- Supra-segmental phonology
Segmental Phonology
Segmental phonology deals with sound segments of language as vowels and consonants and how they make up a syllable. Segmental phonology is not interested in the production or the perception of speech sounds, but it deals with the function of speech sounds and possible combinations of speech sounds within the sound system.
A segment in phonology is any discrete unit that can be identified separately and independently, either auditorily or physically. Segments in phonology refer to phones and phonemes. It studies that how phonemes are made with vowel and consonants and how they perform a function in a language.
Basically segmental phonology encompasses vowels and consonants to explore phonological studies. It deals with the functions of vowels in different words and how letters are formed in a pattern to make a specific sound. The words made and maid are too close in pronunciation however they have different letters. So, segmental phonology is based on the segmentation of language into individual speech sounds.
Supra-segmental Phonology
Supra means ‘above’ or ‘beyond’ and segments are sounds (phonemes). Supra-segmental phonology is also known as prosody. It is concerned with those features of pronunciation that cannot be segmented because they extend over more than one segment, or phonemes. Supra-segmental phonology deals with attributes (like tone, rhythm, stress, etc.) of pronunciation which cannot be segmented. Suprasegmental phonology refers to vocal effects such as stress, tone, intonation, etc. Main suprasegmental features include stress, pitch, tone, intonation or juncture.
Suprasegmental features are meaningful when they are applied above segmental level. Its features are superimposed on the syllables. Stress or accent is the relative emphasis given to a certain syllable in a word, or to a certain word in a phrase or to a certain sentence in a speech. Variations in stress in English are used to distinguish between a noun and a verb e.g. word insult can be used
as a verb and noun and its distinction is the subject of suprasegmental phonology. Supra-segmental features have been explored extensively in the recent era and many theories have been constituted related to the application and description of these features.
Related Posts